Anything you need we are here to help

Shipping and logistics can be complex for international trade. Have you ever wondered how products are classified to ensure accurate tariffs and smooth customs processing? An HTS code (Harmonized Tariff Schedule code) is essential for this, providing a numerical system to classify goods, ensuring proper tariff application and efficient customs handling.
An HTS code stands for Harmonized Tariff Schedule code is a numerical system used to classify products in global trade. It ensures accurate tariff and duty application, regulatory compliance, and efficient customs clearance, facilitating smooth international shipping and trade operations.
By using HTS codes, businesses can avoid delays and penalties associated with incorrect product classification. These codes are part of a global system, streamlining international trade by categorizing goods accurately. Whether you're importing electronics or exporting textiles, knowing the right HTS code is crucial. This guide delves into the structure and assignment of HTS codes, demonstrating their role in facilitating efficient and compliant international trade.
The Harmonized System (HS) is a product classification system managed by the World Customs Organization (WCO). It is used by governments and customs agents globally to identify commodities that are crossing international borders. This standardized method of classification ensures continuity and consistency in global trade processes. From paper and plastics, to fresh produce and hazardous materials, the HS assigns a six-digit code that classifies commodities. Individual countries are able to implement their own additional classification codes for further specifications, which are called Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) codes.
The United States uses a 10-digit HTS code to classify commodities – the first six digits are the universal HS classification number, and the additional four digits represent the Schedule B number, which is assigned by the U.S. Census Bureau’s Foreign Trade Division. All U.S. importers must use the correct HTS code for each commodity they are importing, as duties are calculated based on this classification.
HTS codes, or Harmonized Tariff Schedule codes, are assigned through a systematic process to ensure accurate classification of goods in international trade. The assignment begins with an HTS code lookup, where businesses identify the appropriate category and subcategory for their products. This involves consulting the Harmonized Tariff Schedule, a comprehensive list detailing the classifications and corresponding HTS codes.
Each product is examined based on its material, use, and function, then matched with the six-digit Harmonized System (HS) code. To refine the classification, additional digits are added, specific to national regulations. For instance, the US HTS Code adds four digits to the HS code, detailing further specifications under U.S. trade laws.
Using HTS code lookup tools, businesses can find the correct HTS codes, ensuring compliance with customs regulations and proper tariff applications. Accurate HTS code assignment is crucial for efficient import and export processes, minimizing delays and avoiding costly errors in international trade.
HTS codes, or Harmonized Tariff Schedule codes, are vital for efficient import and export operations. They ensure accurate classification of goods, which is crucial for determining applicable tariffs, duties, and regulations. By using HTS code lookup and HTS codes lookup tools, businesses can identify the correct HTS codes for their products, facilitating compliance with international trade laws.
Proper classification with HTS codes streamlines customs processes, reducing delays and minimizing the risk of penalties or fines. For U.S. businesses, the US HTS Code is particularly important as it includes specific national regulations and duties. Accurate use of the US HTS Code ensures that goods are processed smoothly through U.S. customs, avoiding costly errors and ensuring timely delivery.
In the global market, understanding and utilizing HTS codes effectively enhances operational efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures legal compliance, making them indispensable for any business involved in international trade.
The harmonized tariff schedule streamlines the customs clearance process by classifying products in an organized, standardized system. HTS codes typically consist of 8-to-10 digits, depending on the country. The first six digits of any HTS code are the universal HS classification number, while the remaining digits are subheadings used to designate a country’s specific duty rates.
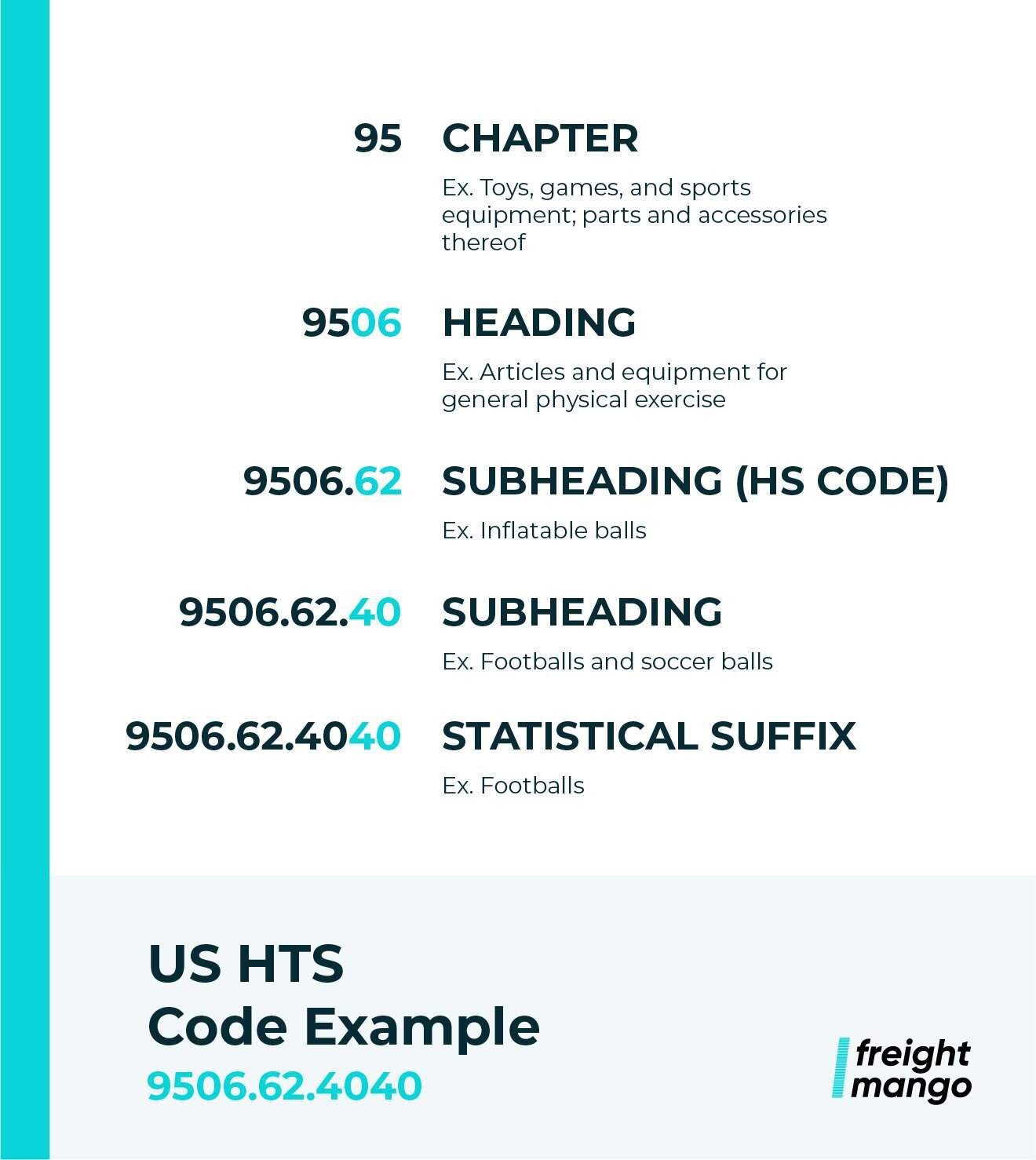
Let’s take a closer look at the elements of a U.S. HTS code, using footballs as an example: HTS Code: 9506.62.4040
The first two numbers in an HS/HTS classification code represent the categorical Chapter. There are currently 99 Chapters in the international HS code list, grouped into 21 general sections.
In our example, footballs are found under Section 20: Miscellaneous Manufactured Articles – Chapter 95: Toys, games, and sports requisites; parts and accessories thereof.
Chapters are further divided into headings, which help narrow down the commodities within the category. In our example, “toys, games, and sports equipment” can be subdivided into, “Articles and equipment for general physical exercise or other sports,” listed under heading “06.”
Headings are then divided into more specific commodity types, listed as subheadings. In our example, subheading 62 is used for the “Inflatables” category.
The combination of the Chapter, Heading, and Subheading classifications make up the universal six-digit HS code that is shared globally. For U.S.-specific classification and duty calculations, we must go a bit further.
The eight-digit subheading, sometimes called a “rate line” is the first subheading unique to the U.S. and helps customs determine specific duties to be paid on the items. In this example, HS subheading for “Inflatables” is further divided into a “Footballs and soccer balls” category.
The final ten-digit “statistical suffix” or “category” is a more detailed description of the item and is used for trade data collection. In our example, footballs and soccer balls are assigned the same amount for duties, but are listed as separate categories for trade data purposes.
Keep in mind that U.S. HTS codes are not recognized in other countries, as each country has their own harmonized tariff schedules that determine duties and taxes. While the six-digit HS classification number should remain the same, any additional digits may indicate a different commodity and ultimately lead to a shipment being rejected at the destination.
Importers bringing goods into the U.S. can use the free Schedule B search tool provided by the U.S. Census Bureau to look up HTS codes. This is the most commonly used method for classifying products due to its simplicity. The tool asks for a description of the commodity and provides several auto-fill suggestions to assist in narrowing down the correct chapter and Schedule B number.
For products that are more difficult to classify, shippers can reference the Customs Rulings Online Search System (CROSS) database. This system is provided by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and is a searchable database of legally binding rulings from other importer and exporter requests for Schedule B codes. This can help determine whether rulings on the same or similar products exist, and what the ruling was.
In the case that no clear Schedule B code can be determined, it is recommended to consult an expert commodity specialist.
Accurate HTS code assignment is crucial for efficient international trade. These codes ensure proper classification of goods, streamline customs processes, and determine applicable tariffs and duties. Using HTS code lookup tools and consulting the Harmonized Tariff Schedule helps businesses find the correct codes, ensuring compliance with regulations. For U.S. imports, the US HTS Code is essential for adherence to national laws. Proper HTS code usage reduces delays, avoids penalties, and facilitates smooth import and export operations, making it a vital aspect of global trade logistics. Understanding and utilizing HTS codes effectively enhances operational efficiency and legal compliance.

