Anything you need we are here to help
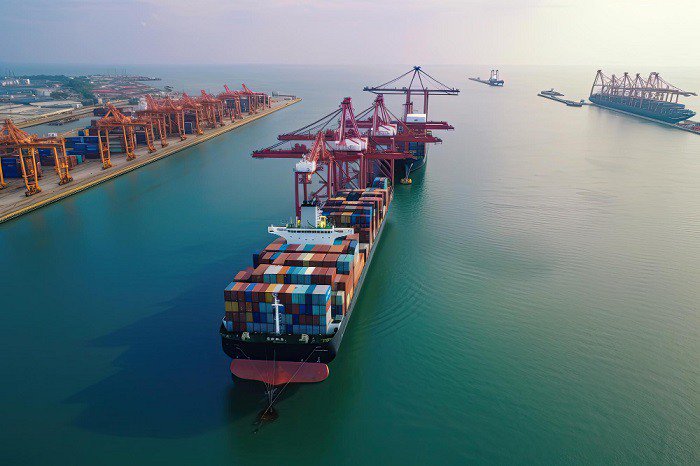


International shipping frequently employs two transport strategies: FCL (Full Container Load) and LCL (Less than Container Load). Although goods are transported across borders in both FCL and LCL shipments, there is a significant difference in the transit times of these two shipping methods when going to the same location.
This variation is influenced by several variables that affect each method's effectiveness, handling, and overall logistics. The reasons why FCL and LCL cargo shipments' transit times differ from one another will be looked at in this blog post.
Let us first establish a clear understanding of FCL and LCL shipments before delving into the causes of the transit time difference.
An FCL shipment is one in which only one shipper or consignee books the entire container. The cargo is the only item in the container; no other shipper's goods are present. This technique is frequently employed when the shipper has enough cargo to fill a container to the brim.
An LCL shipment combines the products of several shippers into a single container. The cargo from each shipper is meticulously separated and packed inside the container. When a shipper's cargo does not fill a whole container, it is preferable to use LCL shipments because sharing container space with other shipments is more economical.
Consolidation and deconsolidation procedures are major factors in the difference in transit times between FCL and LCL shipments. LCL shipments require that the cargo from various shippers be carefully arranged and packed inside the container. The container must then be deconsolidated once it reaches the discharge port to separate the individual shipments for further delivery. Compared to FCL shipments, where the cargo is already loaded and prepared for transport, these extra steps increase complexity and lengthen the overall transit process.
LCL shipments must be handled and sorted carefully several times during loading and unloading. Cargo from various shippers must be accepted, checked, and properly arranged inside the container at the port of origin. The container must also be opened at the port of destination, where the cargo of each shipper must be identified, separated, and organized for delivery. These handling and sorting procedures result in longer transit times for LCL shipments.
The process of clearing customs can differ depending on the type of cargo being shipped, but it is an essential step in international shipping. Since several shippers are involved in LCL shipments, there is a greater chance of running into various cargo types, each with a different clearance requirement. As a result, the transit time may be longer than it would be for FCL shipments, where the customs clearance procedure may be more streamlined. This can cause delays in the customs processing process.
Transit times are significantly influenced by the way shipments are routed. FCL shipments are typically loaded directly onto the vessel without making any stops in between, which streamlines the transportation process. However, intermediate stops at container freight stations may be necessary for LCL shipments to accommodate more cargo and maximize container utilization. These additional stops may increase an LCL shipment's transit time to its destination.
FCL shipments typically receive preference when it comes to loading and unloading. This is so that a single shipper's cargo can be easily distinguished from other shipments because FCL shipments fill the entire container. Because FCL shipments receive priority treatment, loading and unloading times are shortened, reducing transit times.
FCL and LCL cargo shipments have specific uses and benefits in international shipping. Handling and sorting challenges, customs clearance procedures, transportation routing, and delivery prioritization contribute to the difference in transit times between these two methods. LCL shipments offer affordable options for smaller shipments that do not fill an entire container, whereas FCL shipments typically have shorter transit times because of their streamlined processes.
When deciding between FCL and LCL shipments based on their unique needs and priorities, shippers and businesses can make well-informed decisions by understanding the reasons behind the transit time difference.

